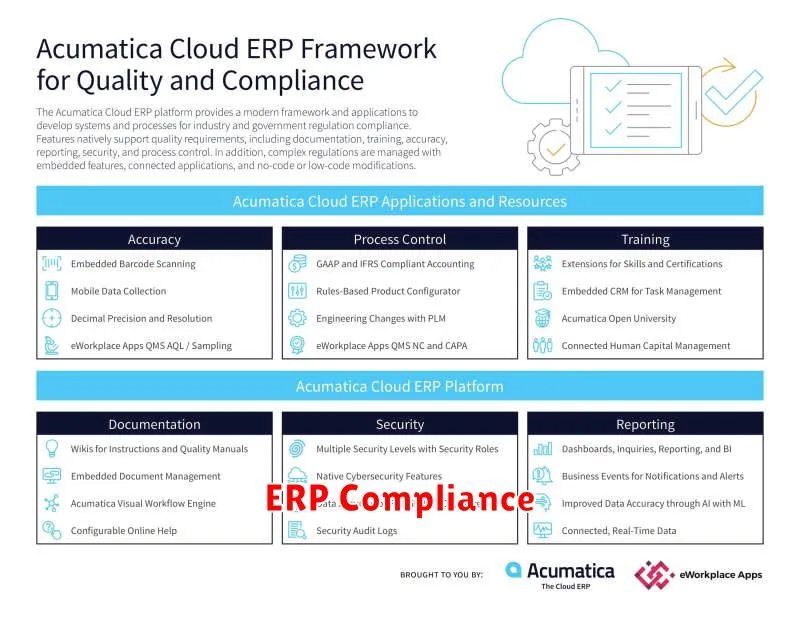
In the dynamic business landscape of 2024, ensuring compliance with ERP software is paramount. From data security to regulatory adherence, staying compliant is crucial for any organization. This article will delve into essential strategies to ensure seamless compliance with your ERP system, protecting your business from potential risks and penalties. Discover how to navigate the evolving regulatory landscape, optimize your ERP implementation for compliance, and establish robust internal controls to mitigate potential vulnerabilities. Join us as we explore the key steps to achieving and maintaining ERP compliance in 2024 and beyond.
Understanding ERP Compliance Requirements
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are critical for businesses of all sizes, providing a centralized platform for managing core business processes. However, with the increasing complexity of data management and regulatory requirements, ensuring ERP compliance has become paramount. This article delves into the essential aspects of ERP compliance, outlining the key requirements and benefits of adhering to them.
Why is ERP Compliance Important?
ERP compliance is not just a matter of ticking off boxes; it’s about protecting your business from various risks, including:
- Financial penalties: Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines from regulatory bodies.
- Reputational damage: Data breaches and security vulnerabilities can severely damage your brand image.
- Operational disruptions: Non-compliant systems can lead to system downtime and data loss, disrupting business operations.
- Legal liabilities: Failure to comply with data privacy regulations can result in legal action from affected parties.
Key ERP Compliance Requirements
The specific ERP compliance requirements vary depending on your industry, location, and the data you handle. However, some common requirements include:
1. Data Security
Protecting sensitive data is crucial. This involves implementing robust access controls, encryption, and regular security audits. Compliance standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS provide guidelines for data security practices.
2. Data Privacy
Ensuring compliance with privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA is vital. This involves obtaining explicit consent for data collection, providing transparent data access policies, and enabling data deletion requests.
3. Auditability and Traceability
Maintaining accurate records and audit trails is crucial for compliance. ERP systems should enable tracking data changes, user actions, and system configurations for regulatory investigations.
4. System Integrity and Availability
Maintaining system uptime and data integrity is essential for business continuity. Implementing disaster recovery plans, regular backups, and system monitoring tools are crucial to ensure system resilience.
Benefits of ERP Compliance
Beyond mitigating risks, ERP compliance offers several benefits:
- Enhanced data security: Protecting your data safeguards your business and customer trust.
- Improved operational efficiency: Compliance often involves streamlining processes and optimizing data management, leading to efficiency gains.
- Increased customer trust: Demonstrating compliance builds trust with customers and partners, fostering stronger relationships.
- Competitive advantage: Compliant businesses have a strong foundation for growth and expansion, giving them a competitive edge.
Conclusion
ERP compliance is an ongoing journey that requires a proactive approach. By understanding the key requirements and implementing robust compliance measures, businesses can mitigate risks, enhance operational efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in today’s data-driven world.
Industry-Specific Regulations
The healthcare industry is heavily regulated, with a complex web of laws and guidelines that govern everything from patient privacy to medical device safety. These regulations are essential for protecting patients, maintaining public health, and ensuring ethical practices. However, navigating this complex landscape can be challenging for healthcare providers.
Data Security and Privacy Standards
In today’s digital age, data is more valuable than ever before. Businesses and individuals alike are constantly generating and storing vast amounts of personal and sensitive information. As a result, data security and privacy have become paramount concerns, leading to the development of numerous standards and regulations to protect this valuable asset.
Data security standards are designed to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. They establish specific guidelines and controls to prevent unauthorized access, modification, or disclosure of information. Some of the most widely recognized data security standards include:
- ISO 27001: This international standard outlines a comprehensive framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continuously improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It covers a wide range of security controls, from physical security to access management and data encryption.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), this framework provides a risk-based approach to cybersecurity, helping organizations to identify, assess, and manage cybersecurity risks. It offers a flexible and adaptable framework that can be tailored to the specific needs of different organizations.
- PCI DSS: The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of requirements designed to protect credit card data. It mandates specific security controls for organizations that store, process, or transmit credit card information.
Data privacy standards focus on protecting personal information from unauthorized use, disclosure, or alteration. They address the collection, storage, use, and sharing of personal data, ensuring that individuals have control over their own information. Key data privacy standards include:
- GDPR: The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive data privacy law implemented by the European Union. It provides individuals with enhanced rights over their personal data, including the right to access, rectify, and erase their data.
- CCPA: The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a landmark data privacy law in the United States. It grants California residents the right to know what personal information businesses collect about them, the right to delete their data, and the right to opt out of the sale of their personal information.
- HIPAA: The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) protects the privacy and security of protected health information (PHI) in the United States. It sets specific requirements for the handling of PHI, including the use of encryption and access controls.
Adhering to these data security and privacy standards is crucial for organizations in today’s digital landscape. By implementing robust security measures and respecting individuals’ privacy rights, businesses can build trust, protect their reputation, and minimize the risks of data breaches and legal penalties. Compliance with these standards is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, assessment, and improvement.
Benefits of Compliant ERP Software
In today’s increasingly regulated business environment, ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations is crucial for any organization. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software can play a significant role in achieving compliance, streamlining processes, and minimizing risk.
Here are some key benefits of using compliant ERP software:
Enhanced Data Security and Privacy
Compliant ERP software incorporates robust security features and data encryption protocols to protect sensitive information. This is essential for industries subject to strict data privacy regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. By centralizing data management and implementing access controls, ERP systems help organizations meet data security requirements and prevent unauthorized access.
Automated Compliance Processes
Many compliance requirements involve repetitive tasks and manual data entry, which can be prone to errors. Compliant ERP software automates these processes, reducing the risk of human error and ensuring consistency. For example, automated workflows can track and manage regulatory reporting, audit trails, and other compliance-related activities.
Improved Financial Reporting and Auditability
Financial reporting is a crucial aspect of compliance. Compliant ERP software provides real-time insights into financial data, allowing for accurate and timely reporting. The integrated nature of ERP systems ensures a consistent and auditable record of financial transactions, facilitating compliance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements.
Streamlined Operations and Efficiency
Compliance often involves complex processes and procedures. Compliant ERP software streamlines these processes, simplifying workflows and improving efficiency. This reduces administrative burden and frees up resources for other critical business activities. For example, automated approval processes and document management systems can expedite compliance activities.
Reduced Risk and Liability
By adhering to compliance regulations and maintaining accurate records, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of fines, penalties, and reputational damage. Compliant ERP software provides a framework for managing compliance risks and helps organizations avoid costly legal issues.
Conclusion
Investing in compliant ERP software is a strategic decision that can yield significant benefits for organizations. From enhanced data security and automated compliance processes to improved financial reporting and reduced risk, compliant ERP systems provide a comprehensive solution for meeting regulatory requirements and achieving operational excellence.
Reduced Risk of Fines and Penalties
Staying compliant with regulations is crucial for any business. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, penalties, and even legal action. By leveraging our services, you can significantly reduce your risk of facing such consequences.
We offer a comprehensive suite of solutions designed to help you maintain regulatory compliance. Our team of experts is well-versed in the latest regulations and can provide guidance on how to meet them effectively. We also offer tools and resources to streamline your compliance processes, making it easier for you to stay on top of your obligations.
By partnering with us, you can gain peace of mind knowing that you are taking the necessary steps to mitigate your risk. We are committed to helping you achieve regulatory compliance and avoid the costly consequences of non-compliance.
Improved Data Accuracy and Integrity
In today’s data-driven world, the accuracy and integrity of data are paramount. Businesses rely on accurate and reliable data for making informed decisions, optimizing operations, and achieving their goals. However, data quality can be compromised by various factors, including human error, data entry mistakes, and inconsistencies in data sources.
To address these challenges, organizations are adopting measures to improve data accuracy and integrity. One key strategy is implementing data quality management (DQM) processes. DQM involves establishing clear data quality standards, defining metrics to measure data accuracy, and implementing procedures to detect and correct data errors.
Data validation is another crucial aspect of data accuracy. This process involves verifying data against predefined rules and constraints to ensure its consistency and correctness. Data validation can be performed at various stages, including data entry, data processing, and data reporting.
In addition to DQM and data validation, organizations can leverage data cleansing techniques to remove inaccurate, incomplete, or duplicate data. Data cleansing involves identifying and correcting errors, standardizing data formats, and enriching data with missing information.
Another approach is data governance, which involves establishing policies and procedures for data management. Data governance aims to ensure data quality throughout its lifecycle, from data collection to data analysis.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can significantly improve data accuracy and integrity, leading to better decision-making, enhanced operational efficiency, and improved customer satisfaction. Accurate and reliable data empowers businesses to gain valuable insights, identify opportunities, and mitigate risks.
Enhanced Business Reputation
In today’s competitive business landscape, maintaining a strong reputation is crucial for success. A positive reputation can attract new customers, build loyalty among existing ones, and enhance brand value.
However, building a strong reputation takes time, effort, and a strategic approach. Here are some key strategies for enhancing your business reputation:
Deliver Exceptional Customer Service
Customer service is at the heart of a positive reputation. Go above and beyond to meet customer expectations and address their concerns promptly and effectively.
Build a Strong Online Presence
Your online presence is often the first impression you make on potential customers. Ensure that your website and social media profiles are professional, informative, and engaging.
Encourage customer reviews and testimonials. Positive feedback can go a long way in building trust and credibility.
Engage in Community Outreach
Get involved in your community through sponsorships, volunteering, or other initiatives. This can demonstrate your commitment to social responsibility and build goodwill among local residents.
Maintain Ethical Practices
Integrity is paramount in building a strong reputation. Operate ethically and transparently, upholding high standards of business conduct.
Address Negative Feedback
No business is perfect. When negative feedback arises, address it professionally and constructively.
Monitor Your Reputation
Regularly monitor your online reputation and address any issues that may arise. Use online reputation management tools to track mentions of your business across various platforms.
By implementing these strategies, you can enhance your business reputation, build stronger relationships with customers, and drive growth for your organization.
Key Features for ERP Compliance

Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are critical for managing and integrating various aspects of a business, from finance and human resources to supply chain and customer relationship management. Ensuring ERP compliance is crucial for organizations to operate effectively, efficiently, and ethically. This article will explore key features that contribute to ERP compliance and highlight their importance.
Data Security and Privacy
Data security and privacy are paramount for ERP compliance. The system should have robust security measures to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, modification, or disclosure. These measures include:
- Access control: Limiting user access to specific data based on their roles and responsibilities.
- Data encryption: Encrypting data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular security audits: Conducting regular audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Data backup and recovery: Implementing robust data backup and recovery plans to prevent data loss.
Auditing and Reporting
An ERP system should provide comprehensive audit trails and reporting capabilities. This enables organizations to track changes, monitor activities, and demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements. Key features include:
- Audit trails: Recording all actions performed within the system, including user logins, data modifications, and approval processes.
- Reporting functionalities: Generating reports on various aspects of operations, such as financial transactions, inventory levels, and customer interactions.
- Data integrity checks: Implementing data integrity checks to ensure data accuracy and completeness.
Regulatory Compliance
ERP compliance extends to meeting specific industry regulations and standards. The system should incorporate features that support compliance with relevant laws and regulations, such as:
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX): Providing tools for financial reporting, internal controls, and audit trails.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Facilitating data subject rights, consent management, and data breach reporting.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): Ensuring compliance with healthcare data privacy and security standards.
User Access and Training
Proper user access management and training are essential for ERP compliance. Organizations should:
- Assign roles and permissions: Granting users appropriate access based on their roles and responsibilities.
- Implement user authentication: Requiring strong passwords and multi-factor authentication.
- Provide comprehensive training: Educating users on system functionality, security practices, and compliance requirements.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
ERP compliance is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and improvement. Organizations should:
- Regularly review and update policies: Ensuring that policies remain aligned with evolving regulations and best practices.
- Monitor system activity: Identifying potential compliance risks and addressing them promptly.
- Implement security patches and updates: Keeping the system secure and up-to-date.
Conclusion
By incorporating these key features, organizations can ensure ERP compliance, minimize risks, and operate effectively. It is important to remember that compliance is not a one-time event but an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and improvement. This ensures that the system remains aligned with evolving regulations and best practices, protecting sensitive data, and fostering a culture of compliance within the organization.
Access Controls and User Permissions
Access controls and user permissions are essential components of any secure system. They ensure that only authorized individuals can access specific resources and perform specific actions. By implementing robust access control mechanisms, organizations can protect sensitive data, prevent unauthorized modifications, and maintain the integrity of their systems.
Access controls are implemented through various methods, including:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assigns permissions to user roles, ensuring consistency and ease of management. For example, administrators might have full access, while employees might have limited access to specific applications.
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): Allows for granular control based on user attributes, such as department, location, or device type. This enables more flexible and context-aware access policies.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): Define specific permissions for individual users or groups for each resource. ACLs provide detailed control over access rights at the object level.
User permissions define the specific actions that users are authorized to perform within the system. These permissions can be granted at various levels, such as:
- Read-Only: Users can view information but cannot modify it.
- Write: Users can create or modify data.
- Delete: Users can remove data.
- Execute: Users can run specific programs or scripts.
By carefully defining and managing access controls and user permissions, organizations can achieve the following benefits:
- Enhanced Security: Reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Improved Compliance: Ensures adherence to regulatory requirements and industry standards.
- Increased Productivity: Enables users to access only the resources they need, improving efficiency.
- Simplified Management: Provides centralized control over access policies, simplifying administration.
In conclusion, access controls and user permissions are crucial for maintaining the security and integrity of any system. By implementing robust access control mechanisms, organizations can safeguard their data, protect their resources, and ensure that only authorized individuals have the necessary permissions to perform their duties.
Audit Trails and Reporting Functionality
Audit trails and reporting functionality are essential features in any system that handles sensitive data or requires accountability for actions. These features provide a detailed record of user activities, system events, and changes made to data. They are crucial for various purposes, including:
- Compliance: Meeting regulatory requirements and industry standards often mandates the tracking of specific activities and data modifications.
- Security: Audit trails help identify and investigate security incidents, unauthorized access attempts, and data breaches.
- Accountability: They provide evidence of who made changes, when they were made, and what the changes were, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Troubleshooting: Audit logs can assist in identifying and resolving system issues, bugs, or errors.
- Business Intelligence: Reporting functionalities can leverage audit data to gain insights into user behavior, system performance, and data usage patterns.
A robust audit trail typically includes information such as:
- User details: Username, user ID, and associated roles or permissions.
- Event timestamp: The date and time of the activity.
- Action performed: Description of the specific action taken, like data access, modification, or deletion.
- Object affected: The specific data or resource involved in the action.
- Source IP address: The location from where the action was initiated.
Reporting functionality allows for the visualization and analysis of audit trail data. Reports can be generated to provide summaries of user activity, system events, and data changes over specific periods. They often include:
- Customizable filters: Allowing users to focus on specific events or actions.
- Graphical representations: Charts, graphs, and dashboards for better understanding and visualization of data.
- Export options: Exporting reports in various formats like CSV, PDF, or Excel for further analysis.
Implementing audit trails and reporting functionality requires careful planning and design. Key considerations include:
- Data retention policy: Determining the duration for which audit data should be retained.
- Security measures: Protecting audit logs from unauthorized access and manipulation.
- Performance impact: Ensuring that audit trail logging does not significantly affect system performance.
- User interface: Providing intuitive and user-friendly reporting tools for analysis.
By implementing comprehensive audit trails and reporting functionality, organizations can enhance security, maintain compliance, improve accountability, and gain valuable insights into their systems and data.
Data Encryption and Backup Solutions
In today’s digital age, data security is paramount. With cyber threats on the rise, it is crucial to implement robust measures to protect sensitive information. Data encryption and backup solutions play a vital role in safeguarding data and ensuring business continuity.
Data Encryption is the process of transforming data into an unreadable format, making it incomprehensible to unauthorized individuals. Encryption algorithms use keys to encrypt and decrypt data, ensuring that only authorized parties can access it. This technology protects data both at rest (stored on devices) and in transit (transmitted over networks).
Data Backup involves creating copies of data and storing them in a separate location. This provides a safety net in case of data loss due to hardware failures, natural disasters, or malicious attacks. Regular backups allow for quick recovery of lost data, minimizing downtime and potential financial losses.
Types of Data Encryption
There are various types of data encryption techniques, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some common types include:
- Symmetric Encryption: Uses the same key for encryption and decryption.
- Asymmetric Encryption: Uses separate keys for encryption and decryption, providing enhanced security.
- Homomorphic Encryption: Allows computations on encrypted data without decrypting it.
Types of Data Backup Solutions
Data backup solutions come in different forms, catering to various needs and budgets. Some common types include:
- Full Backup: Copies all data from the source to the backup location.
- Incremental Backup: Copies only the data that has changed since the last backup.
- Differential Backup: Copies all data that has changed since the last full backup.
- Cloud Backup: Stores backups in a remote data center, providing offsite protection.
Benefits of Data Encryption and Backup Solutions
Implementing data encryption and backup solutions offers numerous benefits, including:
- Data Security: Protects sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Compliance: Ensures compliance with industry regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA.
- Business Continuity: Enables quick recovery from data loss events.
- Reduced Risk: Minimizes the impact of cyber threats and data breaches.
Choosing the right data encryption and backup solutions depends on the specific needs and resources of an organization. It is essential to assess security risks, data sensitivity, and budget constraints before making a decision. By investing in robust data security measures, businesses can protect their valuable assets and ensure business continuity in an increasingly digital world.
Best Practices for Maintaining ERP Compliance
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are the backbone of many businesses, managing critical data and processes. Ensuring compliance with regulations and industry standards is paramount for safeguarding data, mitigating risks, and maintaining a positive business reputation. This article will delve into best practices for maintaining ERP compliance.
1. Establish a Strong Compliance Framework
A robust compliance framework is the cornerstone of any ERP compliance program. It should define roles, responsibilities, policies, and procedures for managing compliance activities.
- Policy Development: Create clear, concise policies that cover data security, access control, audit trails, and other relevant aspects of ERP compliance.
- Risk Assessment: Conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential compliance vulnerabilities and prioritize mitigation strategies.
- Training and Awareness: Provide comprehensive training to employees on ERP compliance policies, procedures, and best practices.
2. Implement Strong Access Control Measures
Unauthorized access to sensitive data can have severe consequences. Implementing strong access controls is essential for safeguarding ERP data:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Grant access based on user roles and responsibilities, ensuring only authorized personnel can access relevant data.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require users to provide multiple authentication factors, such as passwords and one-time codes, for accessing ERP systems.
- Regular Access Reviews: Periodically review user access permissions to ensure they remain appropriate and consistent with current roles and responsibilities.
3. Maintain Comprehensive Audit Trails
Audit trails provide a detailed record of all user actions within the ERP system. This information is crucial for:
- Compliance Reporting: Demonstrating compliance with regulations and industry standards.
- Security Incident Investigations: Tracing unauthorized access or data breaches.
- System Monitoring: Identifying potential security vulnerabilities and anomalies.
4. Regularly Back Up and Recover ERP Data
Data loss can disrupt business operations and lead to significant financial losses. A robust data backup and recovery plan is crucial:
- Regular Backups: Perform frequent backups of ERP data to protect against data loss due to hardware failures, software errors, or cyberattacks.
- Data Recovery Testing: Regularly test data recovery procedures to ensure their effectiveness and identify any shortcomings.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt ERP data backups to protect them from unauthorized access even if they are stolen or compromised.
5. Stay Informed About Evolving Compliance Requirements
Compliance regulations and industry standards are constantly evolving. Staying up-to-date is essential for maintaining ERP compliance:
- Industry News and Publications: Follow industry publications and news sources to stay informed about new compliance requirements and best practices.
- Compliance Audits: Schedule regular compliance audits to identify any gaps in your ERP compliance program.
- Professional Development: Encourage employees involved in ERP management to participate in professional development activities related to compliance.
Conclusion
Maintaining ERP compliance is an ongoing process that requires a commitment to continuous improvement. By implementing these best practices, businesses can safeguard their data, mitigate risks, and foster a culture of compliance within their organization. A robust ERP compliance program is essential for ensuring the long-term security, integrity, and success of any organization.
Regular Software Updates and Patches
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, regular software updates and patches are crucial for maintaining the security, stability, and functionality of our devices and systems. These updates often include vital security fixes, performance enhancements, bug fixes, and new features.
Security Patches are essential for mitigating vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. Cybercriminals are constantly searching for weaknesses in software to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, disrupt operations, or launch attacks. By installing updates promptly, users can stay ahead of these threats and protect their systems from potential harm.
Beyond security, updates also play a significant role in enhancing performance and stability. They often include optimizations that improve system responsiveness, reduce resource consumption, and address bugs that can cause crashes or errors. For example, updates may improve battery life, speed up application loading times, or enhance the overall user experience.
New Features are sometimes included in software updates, providing users with access to enhanced functionality or capabilities. These additions can range from minor improvements to significant new tools and services, expanding the possibilities of what users can achieve with their software.
While updates are generally beneficial, it’s essential to be mindful of the potential risks associated with installing them. Some updates may introduce new bugs or compatibility issues, so it’s always wise to back up important data before proceeding. However, the benefits of staying up-to-date far outweigh the risks, ensuring a secure, stable, and feature-rich computing experience.
Employee Training on Compliance Policies
In today’s complex business environment, it’s more important than ever for companies to have robust compliance programs in place. These programs are designed to ensure that businesses operate ethically and legally, adhering to all applicable laws and regulations. A crucial component of any effective compliance program is comprehensive employee training.
Employee training on compliance policies serves several vital purposes. First and foremost, it helps to educate employees about the company’s expectations and the legal and ethical standards they are required to uphold. This knowledge empowers employees to make informed decisions and avoid potential violations. By understanding the company’s policies, employees can better recognize and address potential compliance risks.
Furthermore, effective employee training on compliance policies helps to foster a culture of compliance within the organization. When employees are well-informed about the rules and regulations, they are more likely to take them seriously and incorporate them into their daily work practices. This shared understanding of compliance expectations creates a strong foundation for ethical and legal behavior throughout the company.
Another key benefit of employee training is that it helps to mitigate risks and protect the company from legal and financial consequences. By ensuring that employees are aware of and comply with all applicable laws and regulations, companies can reduce their exposure to fines, lawsuits, and other penalties. This proactive approach to compliance can save businesses significant time, money, and resources in the long run.
When designing employee training programs, it’s important to tailor the content to the specific needs and roles of different employees. The training should be engaging, interactive, and easily accessible. Utilizing a variety of learning methods, such as online courses, webinars, and interactive simulations, can help to keep employees engaged and ensure that they retain the information. Regular refresher training sessions are also essential to reinforce compliance principles and keep employees up-to-date on any changes to policies or regulations.
Investing in comprehensive employee training on compliance policies is a wise decision for any organization. By educating employees and fostering a culture of compliance, companies can protect themselves from legal and financial risks, enhance their reputation, and create a more ethical and responsible workplace.
Ongoing Monitoring and Audits
Ongoing monitoring and audits are crucial for ensuring that an organization’s operations are compliant with relevant regulations, policies, and standards. They provide a mechanism for identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities, assessing the effectiveness of controls, and implementing corrective actions to mitigate any identified issues.
Benefits of Ongoing Monitoring and Audits
There are numerous benefits associated with ongoing monitoring and audits, including:
- Improved Compliance: Regular monitoring and audits help ensure that the organization is adhering to all applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards.
- Reduced Risk: By identifying and addressing potential risks early on, organizations can significantly reduce their exposure to financial, operational, and reputational losses.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Ongoing monitoring can streamline processes, identify areas for improvement, and optimize resource allocation.
- Increased Transparency and Accountability: Regular audits promote transparency and accountability by providing stakeholders with assurance that operations are conducted ethically and effectively.
Key Aspects of Ongoing Monitoring and Audits
Effective ongoing monitoring and audits involve several key aspects:
- Scope and Frequency: Determining the scope and frequency of monitoring and audits depends on the organization’s specific risks and vulnerabilities. High-risk areas should be monitored more frequently.
- Methodology: The methodology used for monitoring and auditing should be appropriate for the organization’s size, complexity, and industry. It may include data analysis, interviews, document reviews, and site visits.
- Documentation: All monitoring and audit findings should be documented, along with any corrective actions taken. This documentation serves as a record of compliance efforts and helps track progress over time.
- Reporting: Regularly reporting on the findings of ongoing monitoring and audits to relevant stakeholders is crucial for ensuring accountability and driving improvements.
Conclusion
Ongoing monitoring and audits are essential for maintaining compliance, mitigating risks, and ensuring the overall effectiveness of an organization’s operations. By implementing a comprehensive program that addresses key aspects such as scope, methodology, documentation, and reporting, organizations can reap the benefits of improved compliance, reduced risk, enhanced efficiency, and increased transparency and accountability.